PayPal is the latest company to report a data breach, but it’s certainly not the only one. With cyber threat actors targeting big corporations, software companies and even apps on your phone, your personal data could be at risk. If your private information has been compromised, you often won’t learn about it until a company notifies you about a data breach. By that time your birthday, Social Security number, credit card number or health records will have already been exposed or stolen. (Here’s what to do if you think your Social Security number was stolen in the PayPal breach.)
Any stolen information that leads data thieves to your identity can let hackers do everything, from making purchases and opening up credit accounts in your name, to filing for your tax refunds and making medical claims posing as you. Billions of these hacked login credentials are available on the dark web, neatly packaged for hackers to easily download for free.
You can’t stop sites from getting hacked, but after a cyberattack, monitoring tools can alert you to which of your stolen credentials are out on the dark web, giving you a running start at limiting the damage the thieves can do. Here’s how to use two free monitoring tools — Google’s Password Checkup and Mozilla’s Firefox Monitor — to see which of your email addresses and passwords are compromised so you can take action.
Steps you can take before a data breach
First, use a password manager that creates unique passwords for each of your logins and make sure you are following password best practices. That way, if one site gets breached, your stolen password won’t give hackers access to your accounts on other sites. A good password manager can help you administer all your login information, making it easy to create and use unique passwords.
And once you find out a company or service with your credentials has been hacked, change that password, regardless if you are notified that your information was exposed in the data breach or not. You don’t want to wait days to act while the company works to uncover the extent of the hack.
How to use Google’s Password Checkup
As part of its password manager service,Google offers the free Password Checkup tool, which monitors usernames andpasswords you use to sign in to sites outside of Google’s domain andnotifies you if those login credentials have been exposed. (You mayremember Password Checkupwhen it was a Chrome extension you had to add separately to Google’sbrowser. This is the same tool folded into Google’s password manager.)


Google’s Password Checkup finds a few password problems.
Screenshot by Clifford Colby/CNET1. If you use Google’s password service to keep track of your login credentials in Chrome or Android, head to Google’s password manager site and tap Go to Check passwords.
2. Tap Check Passwords and verify it’s you.
3. Enter the password for your Google account.
4. After thinking for a bit, Google will display any issues it’s found, including compromised, reused and weak passwords.
5. Next to each reused or weak password is a Change password button you can tap to pick a more secure one.
How to use Mozilla’s Firefox Monitor
Mozilla’s free Firefox Monitor service helps you track which of your email addresses have been part of known data breaches.
1. To start, head to the Firefox Monitor page.
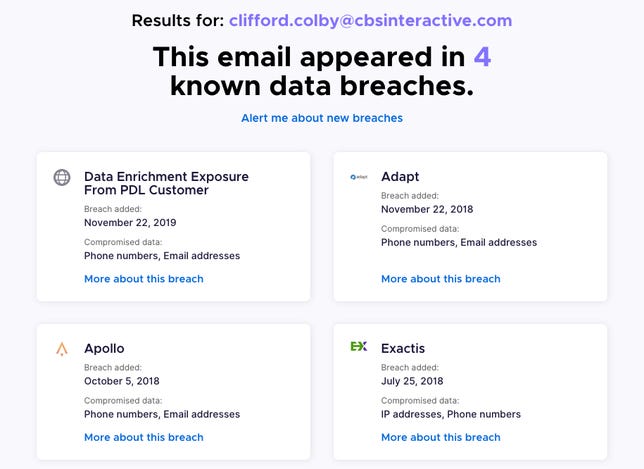

Mozilla’s Firefox Monitor identified four breaches for this email.
Screenshot by Clifford Colby/CNET2. Enter an email address and tap Check for Breaches. If the email was part of a known breach since 2007, Monitor will show you which hack it was part of and what else may have been exposed.
3. Below a breach, tap More about this breach to see what was stolen and what steps Mozilla recommends, such as updating your password.
You can also sign up to have Monitor notify you if your email is involved in a future data breach. Monitor scans your email address against those found data breaches and alerts you if you were involved.
1. Near the bottom of the Firefox Monitor page, tap the Sign up for Alerts button.
2. If you need to, create a Firefox account.
3. Tap Sign in to see a breach summary for your email.
4. At the bottom of the page, you can add additional email addresses to monitor. Mozilla will then send you an email at each address you add with a subject line “Firefox Monitor found your info in these breaches” when it finds that email address involved in a breach, along with instructions about what to do about following the breach.
How else to watch for fraud
Besides using the tools from Mozilla and Google, you can take a few more steps to watch for fraud.
View your digital footprint. Bitdefender provides a dashboard with its Digital Identity Protection subscription that shows where your personal information has appeared online. It also pinpoints data breaches where your info has been leaked in the past, notifies you when your personal info appears in breaches going forward and provides recommended steps to secure your data. It also tells you whether your info is on the dark web and lets you know if someone appears to be impersonating you on social media.
Monitor your credit reports. To help you spot identity theft early, you can request one free credit report a year from each of the three major credit bureaus — Equifax, Experian and TransUnion — to check for unfamiliar activity, such as a new account you didn’t open. You should also check your credit card and bank statements for unexpected charges and payments. Unexpected charges can be a sign that someone has access to your account.
Sign up for a credit monitoring service. To take a more active hand in watching for fraud, sign up with a credit monitoring service that constantly monitors your credit report on major credit bureaus and alerts when it detects unusual activity. With a monitoring service, you can set fraud alerts that notify you if someone is trying to use your identity to create credit. A credit reporting service like LifeLock can cost $9 to $24 a month — or you could use a free service like the one from Credit Karma that will watch for credit fraud but not ID fraud, such as someone trying to use your Social Security number.
For more on how to keep your data secure, see our guides on how to protect your phone’s privacy, the best VPN services and why you should never trust a free VPN.

